Download High-quality and well-structured notes of “Human Anatomy and Physiology” in pdf – Bpharm 1st Semester – STANDARD NOTES.
Here you can download all units of Human Anatomy and Physiology (BP101T). These notes cover all the important topics with diagrams and are very easy to download.
Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Notes
UNIT – 1
Introduction to human body, Cellular level of organization, Tissue level of organization
UNIT – 2
Integumentary system, Skeletal system, Joints
UNIT – 3
Body fluids and blood, Lymphatic system

UNIT – 4
Peripheral nervous system, Special senses
UNIT – 5
Cardiovascular system
Scope of Human Anatomy and Physiology 1
This subject is designed to impart fundamental knowledge on the structure and
functions of the various systems of the human body. It also helps in understanding both
homeostatic mechanisms. The subject provides the basic knowledge required to
understand the various disciplines of pharmacy.
Objectives of Human Anatomy and Physiology 1
Upon completion of this course the student should be able to
- Explain the gross morphology, structure and functions of various organs of the human
body. - Describe the various homeostatic mechanisms and their imbalances.
- Identify the various tissues and organs of different systems of human body.
- Perform the various experiments related to special senses and nervous system.
- Appreciate coordinated working pattern of different organs of each system.
Syllabus of Human Anatomy and Physiology 1
UNIT – 1
Introduction to human body
Definition and scope of anatomy and physiology, levels of structural
organization and body systems, basic life processes, homeostasis, basic
anatomical terminology.
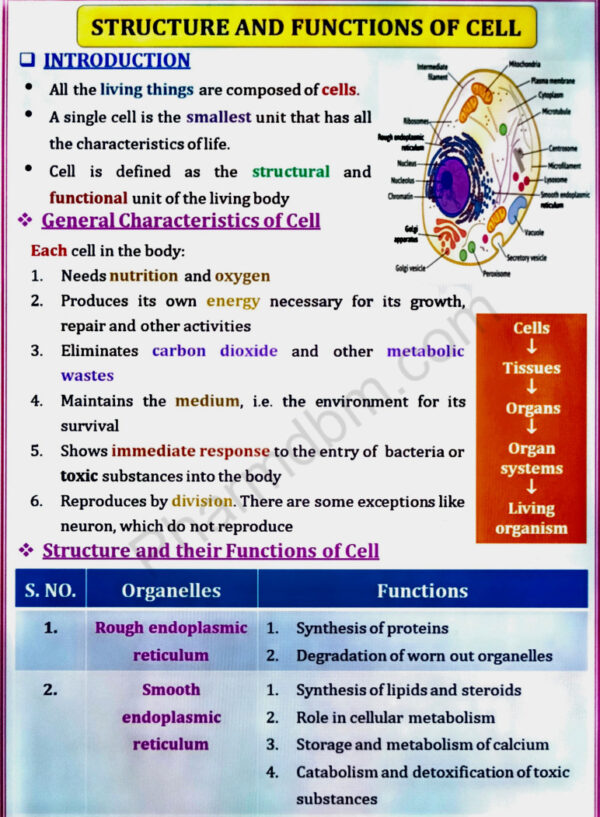
Cellular level of organization
Structure and functions of cell, transport across cell membrane, cell
division, cell junctions. General principles of cell communication,
intracellular signaling pathway activation by extracellular signal
molecule, Forms of intracellular signaling: a) Contact-dependent b)
Paracrine c) Synaptic d) Endocrine
Tissue level of organization
Classification of tissues, structure, location and functions of epithelial,
muscular and nervous and connective tissues
UNIT – 2
Integumentary system
Structure and functions of skin
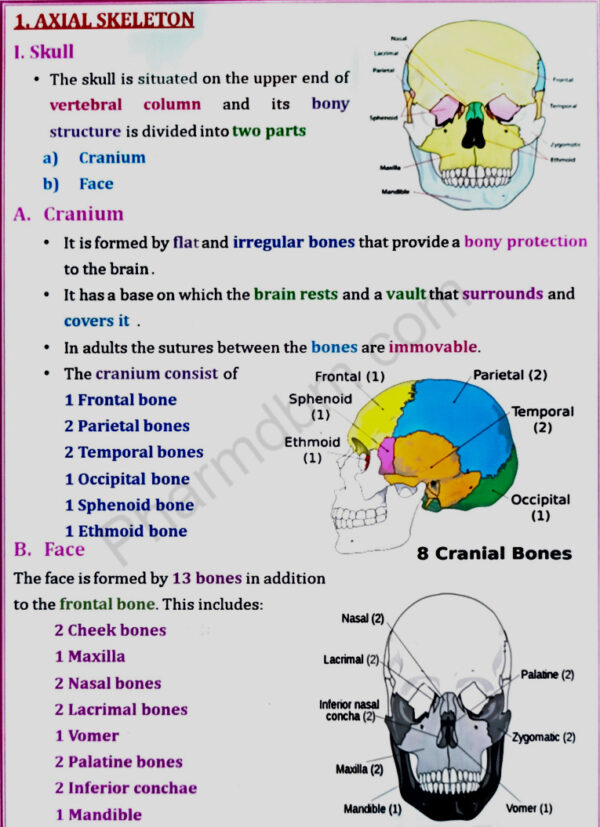
Skeletal system
Divisions of skeletal system, types of bone, salient features and functions
of bones of axial and appendicular skeletal system
Organization of skeletal muscle, physiology of muscle contraction,
neuromuscular junction
Joints
Structural and functional classification, types of joints movements and its
articulation
UNIT – 3
Body fluids and blood
Body fluids, composition and functions of blood, hemopoeisis, formation of
hemoglobin, anemia, mechanisms of coagulation, blood grouping, Rh factors,
transfusion, its significance and disorders of blood, Reticulo endothelial system.
Lymphatic system
Lymphatic organs and tissues, lymphatic vessels, lymph circulation and functions of
lymphatic system
UNIT – 4
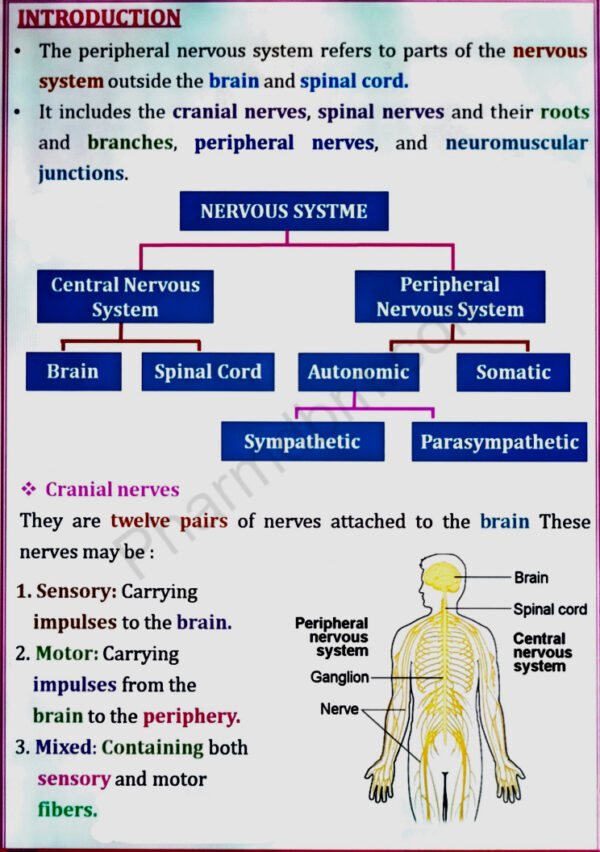
Peripheral nervous system
Classification of peripheral nervous system: Structure and functions of
sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system.
Origin and functions of spinal and cranial nerves.
Special senses
Structure and functions of eye, ear, nose and tongue and their disorders.
UNIT – 5
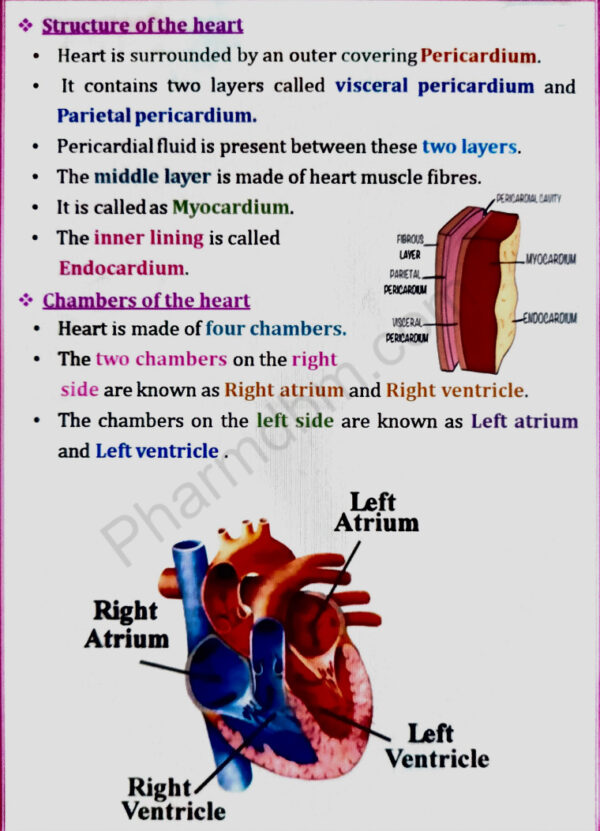
Cardiovascular system
Heart – anatomy of heart, blood circulation, blood vessels, structure and functions of
artery, vein and capillaries, elements of conduction system of heart and heart beat, its
regulation by autonomic nervous system, cardiac output, cardiac cycle. Regulation of
blood pressure, pulse, electrocardiogram and disorders of heart.


