Free Download Pharmaceutical Analysis Notes in pdf – Bpharm 1st Semester. High quality, well-structured and Standard Notes that are easy to remember.
Welcome to Pharmdbm.com
Pharmdbm provides standard or well-structured Notes for Bpharm students. The notes are free to download. Each semester notes of Bpharm are available on www.pharmdbm.com.
In this post you can download notes of Pharmaceutical Analysis (BP102T). All units are available to download for free.
Pharmaceutical Analysis Notes Unit 1 – 5
UNIT – 1
Introduction of Pharmaceutical analysis, Pharmaceutical Errors, Pharmacopoeia-Sources of impurities in medicinal agents & limit test

UNIT – 2
Acid base titration, Non aqueous titration

UNIT – 3
Precipitation titrations, Complexometric titration, Gravimetric & diazotisation titration

UNIT – 4
Redox titrations
UNIT – 5
Electrochemical methods of analysis – Conductometry, Potentiometry, Polarography
Scope of Pharmaceutical Analysis
This course deals with the fundamentals of analytical chemistry and principles of
electrochemical analysis of drugs.
Objectives of Pharmaceutical Analysis
Upon completion of the course student shall be able to –
- Understand the principles of volumetric and electro chemical analysis
- Carryout various volumetric and electrochemical titrations.
- Develop analytical skills.
Syllabus of Pharmaceutical Analysis
UNIT – 1
(a) Pharmaceutical analysis– Definition and scope
i) Different techniques of analysis
ii) Methods of expressing concentration
iii) Primary and secondary standards.
iv) Preparation and standardization of various molar and normal solutions- Oxalic acid, sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, sodium thiosulphate, sulphuric acid, potassium permanganate and ceric ammonium sulphate
(b)Errors: Sources of errors, types of errors, methods of minimizing errors,
accuracy, precision and significant figures
(c)Pharmacopoeia, Sources of impurities in medicinal agents,limit tests.
UNIT – 2
Acid base titration: Theories of acid base indicators, classification of
acid base titrations and theory involved in titrations of strong, weak, and
very weak acids and bases, neutralization curves
Non aqueous titration: Solvents, acidimetry and alkalimetry titration and
estimation of Sodium benzoate and Ephedrine HCl
UNIT – 3
Precipitation titrations: Mohr’s method, Volhard’s, Modified
Volhard’s, Fajans method, estimation of sodium chloride.
Complexometric titration: Classification, metal ion indicators, masking
and demasking reagents, estimation of Magnesium sulphate, and calcium
gluconate.
Gravimetry: Principle and steps involved in gravimetric analysis. Purity
of the precipitate: co-precipitation and post precipitation, Estimation of
barium sulphate.
Basic Principles,methods and application of diazotisation titration.
UNIT – 4
Redox titrations
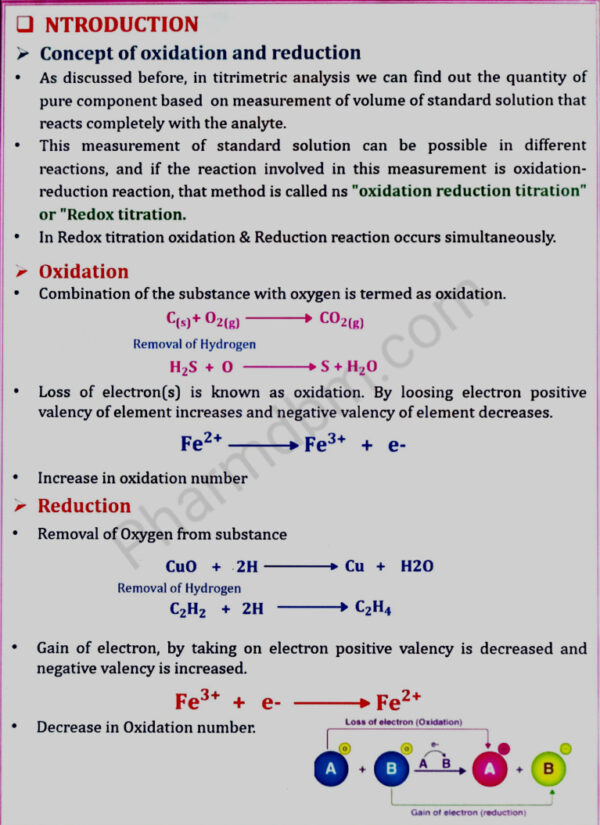
(a) Concepts of oxidation and reduction
(b) Types of redox titrations (Principles and applications)
Cerimetry, Iodimetry, Iodometry, Bromatometry, Dichrometry, Titration with
potassium iodate
UNIT – 5
Electrochemical methods of analysis
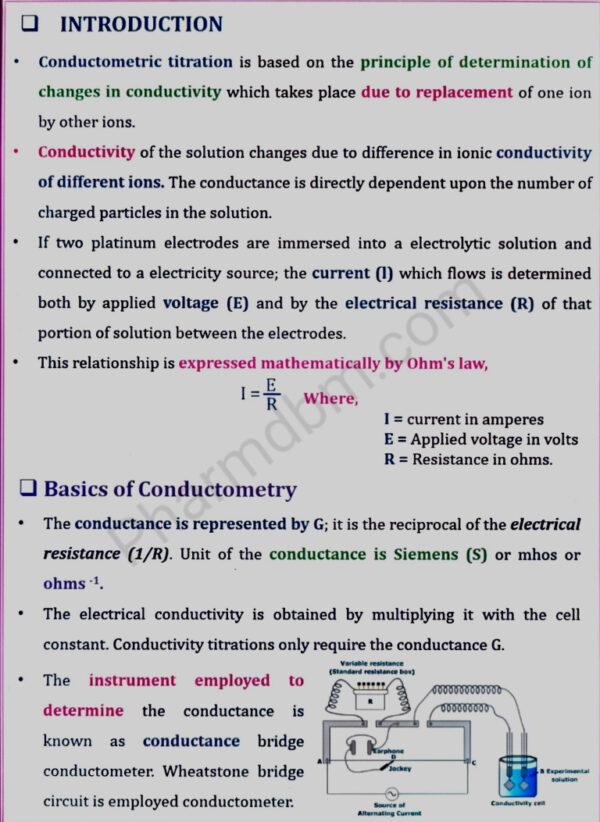
Conductometry– Introduction, Conductivity cell, Conductometric
titrations, applications.
Potentiometry – Electrochemical cell, construction and working
of reference (Standard hydrogen, silver chloride electrode and
calomel electrode) and indicator electrodes (metal electrodes and
glass electrode), methods to determine end point of potentiometric
titration and applications.
Polarography – Principle, Ilkovic equation, construction and
working of dropping mercury electrode and rotating platinum
electrode, applications


