
Download High-quality and well-structured notes of Instrumental Methods of Analysis in pdf for Bpharm 7th-Semester students.
Here you can download all units of Instrumental Methods of Analysis (BP701T). These notes cover all the important topics with diagrams and are very easy to download.
Instrumental Method of Analysis Notes Unit 1 – 5
UNIT – 1
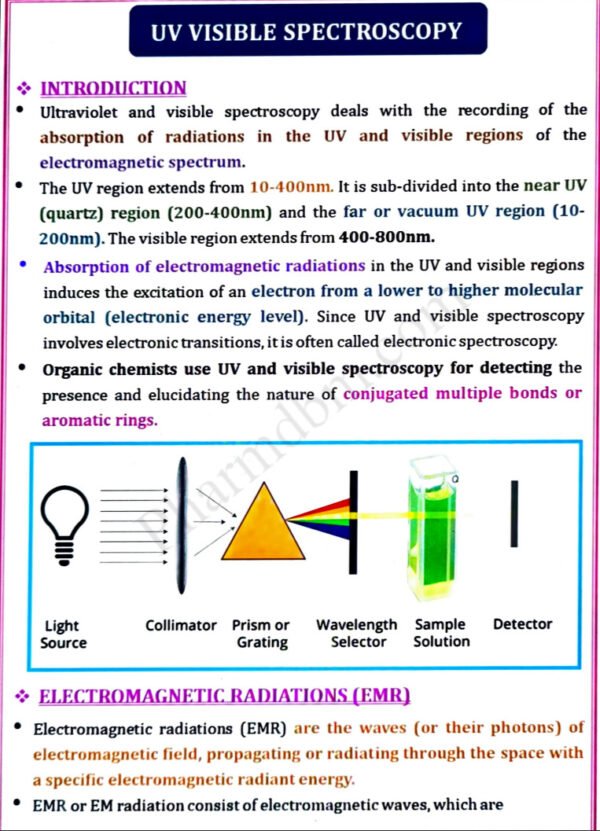
UV Visible spectroscopy
Fluorimetry
UNIT – 2
IR Spectroscopy, Flame Photometry, Atomic absorption spectroscopy, Nepheloturbidometry

UNIT – 3
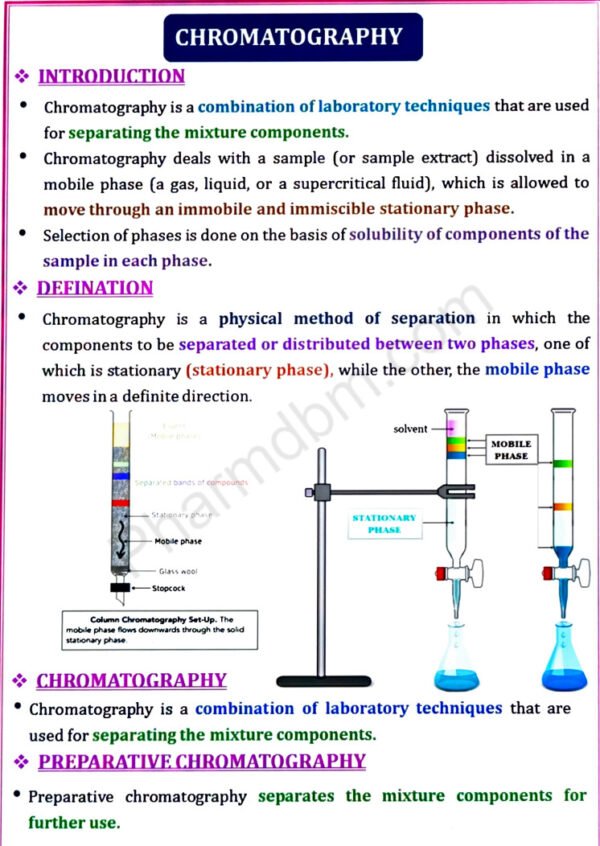
Introduction of chromatography, Adsorption and partition column chromatography, Thin layer chromatography, Paper chromatography, Electrophoresis
UNIT – 4
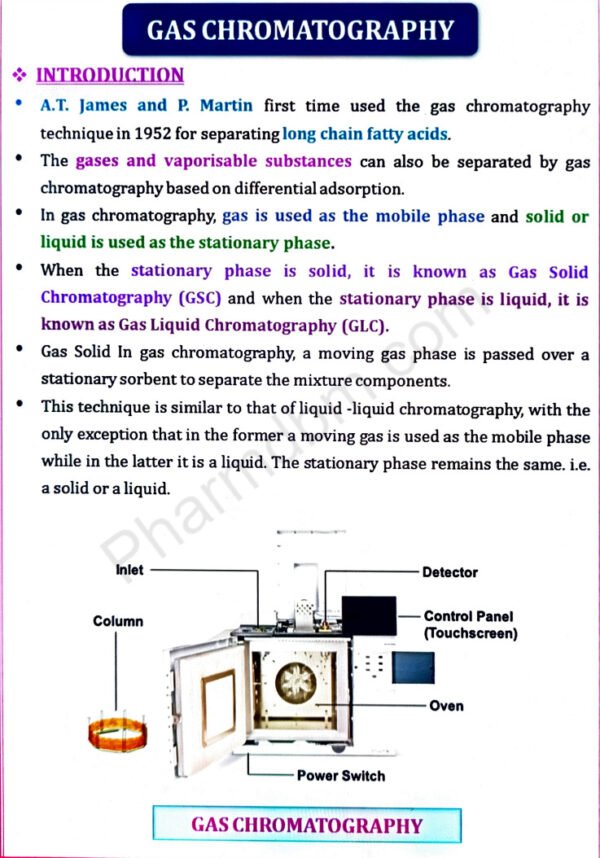
Gas chromatography, High performance liquid chromatography
UNIT – 5
Ion exchange chromatography, Gel chromatography, Affinity chromatography

Bpharm 7th Semester
Instrumental Methods of Analysis
Novel Drug Delivery Systems
Industrial Pharmacy 2
Pharmacy Practice
Scope of Instrumental Methods of Analysis
This subject deals with the application of instrumental methods in qualitative and
quantitative analysis of drugs. This subject is designed to impart a fundamental
knowledge on the principles and instrumentation of spectroscopic and chromatographic
technique. This also emphasizes on theoretical and practical knowledge on modern
analytical instruments that are used for drug testing.
Objectives of Instrumental Methods of Analysis
Upon completion of the course the student shall be able to:
- Understand the interaction of matter with electromagnetic radiations and its
applications in drug analysis - Understand the chromatographic separation and analysis of drugs.
- Perform quantitative & qualitative analysis of drugs using various analytical
instruments.
Syllabus of Instrumental Methods of Analysis
UNIT – 1
UV Visible spectroscopy
Electronic transitions, chromophores, auxochromes, spectral shifts, solvent effect on
absorption spectra, Beer and Lambert’s law, Derivation and deviations.
Instrumentation – Sources of radiation, wavelength selectors, sample cells, detectors- Photo tube, Photomultiplier tube, Photo voltaic cell, Silicon Photodiode. Applications – Spectrophotometric titrations, Single component and multi component
analysis
Fluorimetry
Theory, Concepts of singlet, doublet and triplet electronic states, internal and external
conversions, factors affecting fluorescence, quenching, instrumentation and
applications
UNIT – 2
IR spectroscopy
Introduction, fundamental modes of vibrations in poly atomic molecules, sample
handling, factors affecting vibrations
Instrumentation – Sources of radiation, wavelength selectors, detectors – Golay cell,
Bolometer, Thermocouple, Thermister, Pyroelectric detector and applications
Flame Photometry-Principle, interferences, instrumentation and applications
Atomic absorption spectroscopy– Principle, interferences, instrumentation and
applications
Nepheloturbidometry– Principle, instrumentation and applications
UNIT – 3
Introduction to chromatography
Adsorption and partition column chromatography-Methodology, advantages,
disadvantages and applications.
Thin layer chromatography– Introduction, Principle, Methodology, Rf values,
advantages, disadvantages and applications.
Paper chromatography-Introduction, methodology, development techniques,
advantages, disadvantages and applications
Electrophoresis– Introduction, factors affecting electrophoretic mobility, Techniques
of paper, gel, capillary electrophoresis, applications
UNIT – 4
Gas chromatography – Introduction, theory, instrumentation, derivatization, temperature programming, advantages, disadvantages and applications
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-Introduction, theory, instrumentation, advantages and applications.
UNIT – 5
Ion exchange chromatography– Introduction, classification, ion exchange resins, properties, mechanism of ion exchange process, factors affecting ion exchange, methodology and applications
Gel chromatography– Introduction, theory, instrumentation and applications
Affinity chromatography– Introduction, theory, instrumentation and applications


